Published: October 2022
Last Reviewed: November 2025
In this article, learn about the different phases of wound healing that take place and why each stage is required to enable proper wound healing.

Published: October 2022
Last Reviewed: November 2025
Hemostasis (blood clotting)
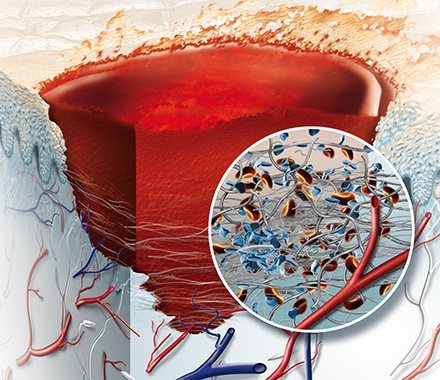
The first stage of wound healing is the hemostasis stage, which is crucial for stopping bleeding immediately after an injury. During this stage, blood vessels constrict to reduce blood flow, allowing blood clotting to begin.
Platelets gather at the wound site and stick together to form a clot, acting as a temporary plug to protect the wound and prevent further blood loss. Understanding the hemostasis stage is key to effective wound care and faster recovery.
This stage may take up to two days for larger wound.
Inflammation (preventing infection)
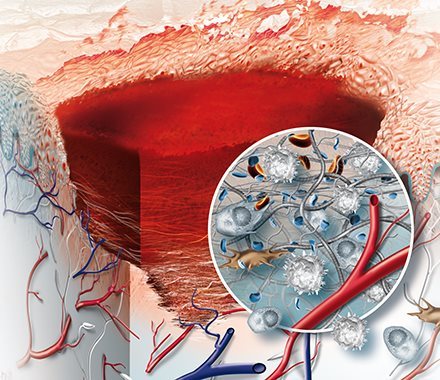
Once bleeding has stopped, the next stage of wound healing is inflammation. This stage starts a few hours after an injury and can last two to five days. During this time, the body works to protect the wound and prevent infection.
Blood vessels widen to allow white blood cells to reach the area, removing bacteria, debris, and damaged cells. This can cause redness, swelling, warmth, and pain, which are normal signs that your body is healing. Some discomfort is normal as blood rushes to the wound to clean it.
Proliferation (rebuilding)
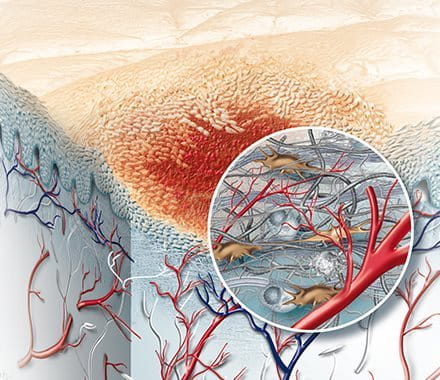
The proliferation phase is the next stage after the wound has been cleaned. During this phase, the body focuses on repairing and rebuilding tissue, and it can be broken down into three key steps:
This phase can last anywhere from four to 30 days, depending on the size and severity of the wound, and is essential for restoring the skin's strength and integrity.
Maturation (strengthening)
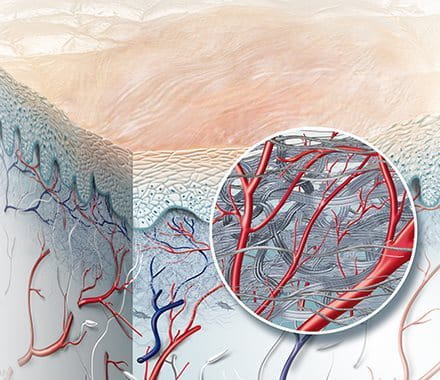
Maturation is the longest of the four stages of wound healing. It usually begins around three weeks after the injury and, in some cases, can take over a year for the tissue to fully repair.
At this stage, the repair cells used in the proliferation phase are no longer needed, so they are removed through apoptosis. Meanwhile, the new tissue that formed during proliferation begins to gain strength and flexibility. Water is reabsorbed, allowing collagen fibres to lie closer together and form a stronger, more organised structure.
If a wound becomes infected, healing is slowed and disrupted at all stages, from prolonged inflammation to delayed tissue formation and weaker final tissue, preventing efficient repair. This happens because the immune system focuses on fighting bacteria rather than progressing through the normal healing stages.
It’s important to seek medical attention if signs of infection appear, such as increased redness, swelling, pain, or pus.
After understanding the stages of wound healing, it’s important to follow the right wound care routine to help your wound heal safely and quickly:
1. Cleanse

Wound cleansing is the first and most important step in proper wound care. Gently cleanse your wound of dirt, bacteria, and visible particles with Elastoplast Wound Spray to help prevent infection and support faster healing.
Even minor wounds can become infected if not cleaned correctly. Elastoplast Wound Spray offers easy, effective, and antiseptic cleansing for cuts, grazes, burns, and blisters through a gentle spray action, helping you care for your skin safely and comfortably.
2. Protect

Elastoplast Second Skin Hydrocolloid Plaster provides both protection and care for everyday wounds. Its waterproof, discreet patches form a protective barrier that keeps the wound clean and promotes faster healing. Read more about the benefits of hydrocolloid plasters here.
For larger wounds, try the Elastoplast Sterile Waterproof XL MED+ Dressing. It offers reliable waterproof protection for bigger or post-operative wounds, with an extra-large, non-stick wound pad that cushions the area and provides all-day comfort.
3. Heal
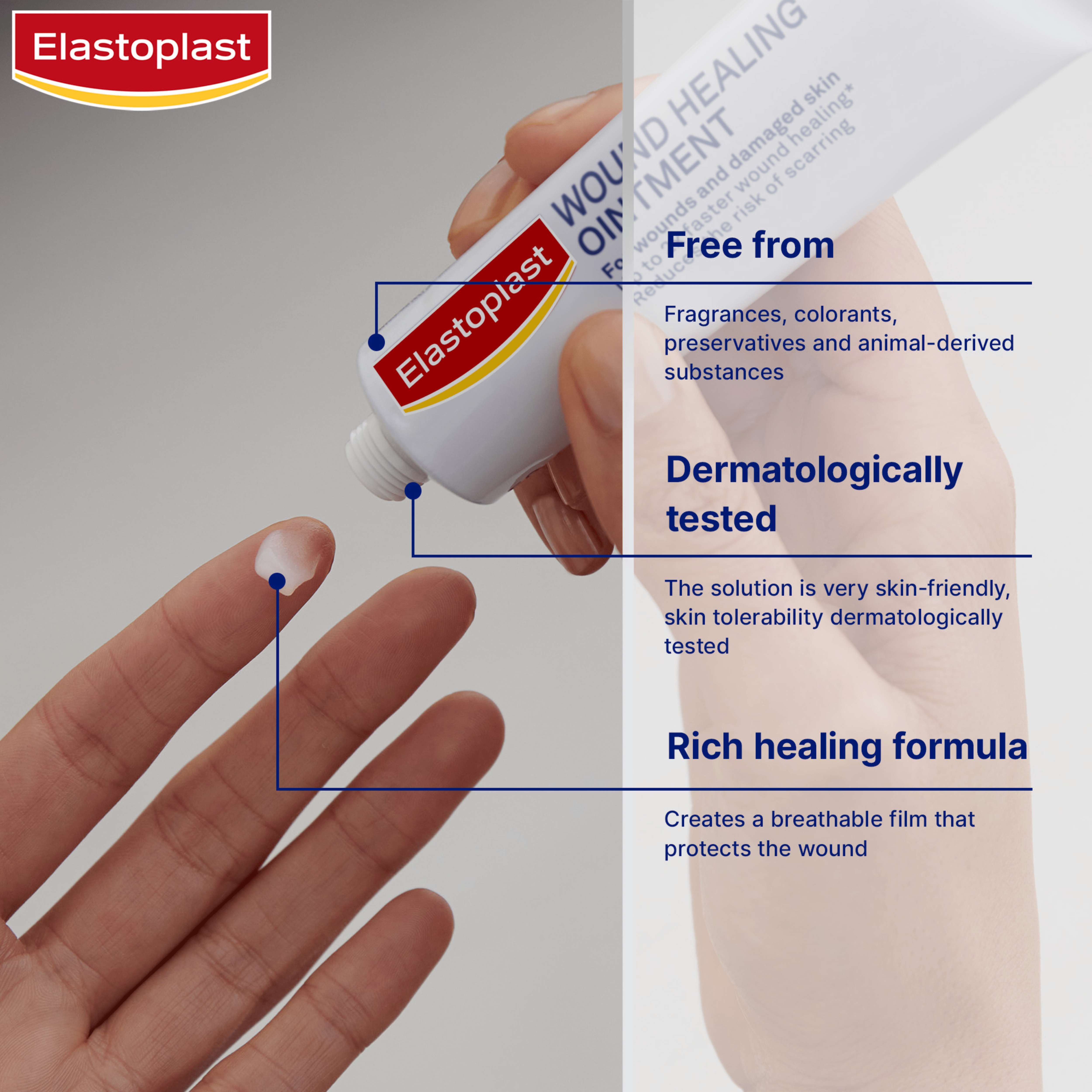
Applying a wound healing ointment to cuts or grazes is an important step in recovery. It forms a protective barrier that keeps out dirt and bacteria while supporting faster healing.
Elastoplast Wound Healing Ointment helps wounds heal up to 2x faster while preventing dryness. Clinically proven to support natural healing and reduce scarring, it is safe for babies and sensitive skin at any stage of healing and is also dermatologically tested for gentle care.
What are good signs of wound healing?
What indicates poor wound healing?
Poor wound healing is often indicated by persistent or worsening symptoms instead of gradual improvement. Signs include:
These signs suggest that the healing process has slowed or become disrupted, possibly due to infection, poor circulation, or underlying health conditions. If a wound isn’t improving or appears to be getting worse, contact a healthcare professional immediately.