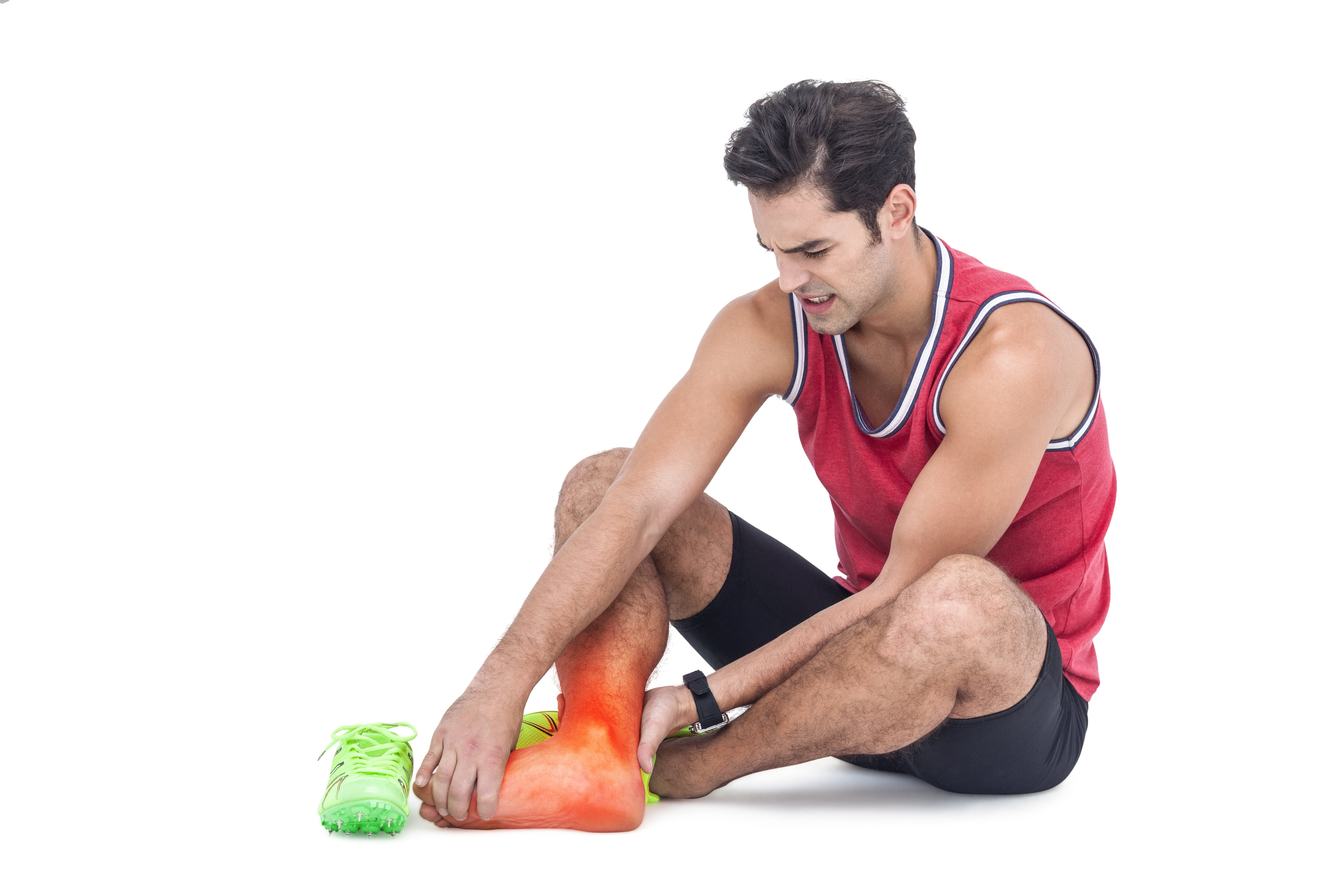
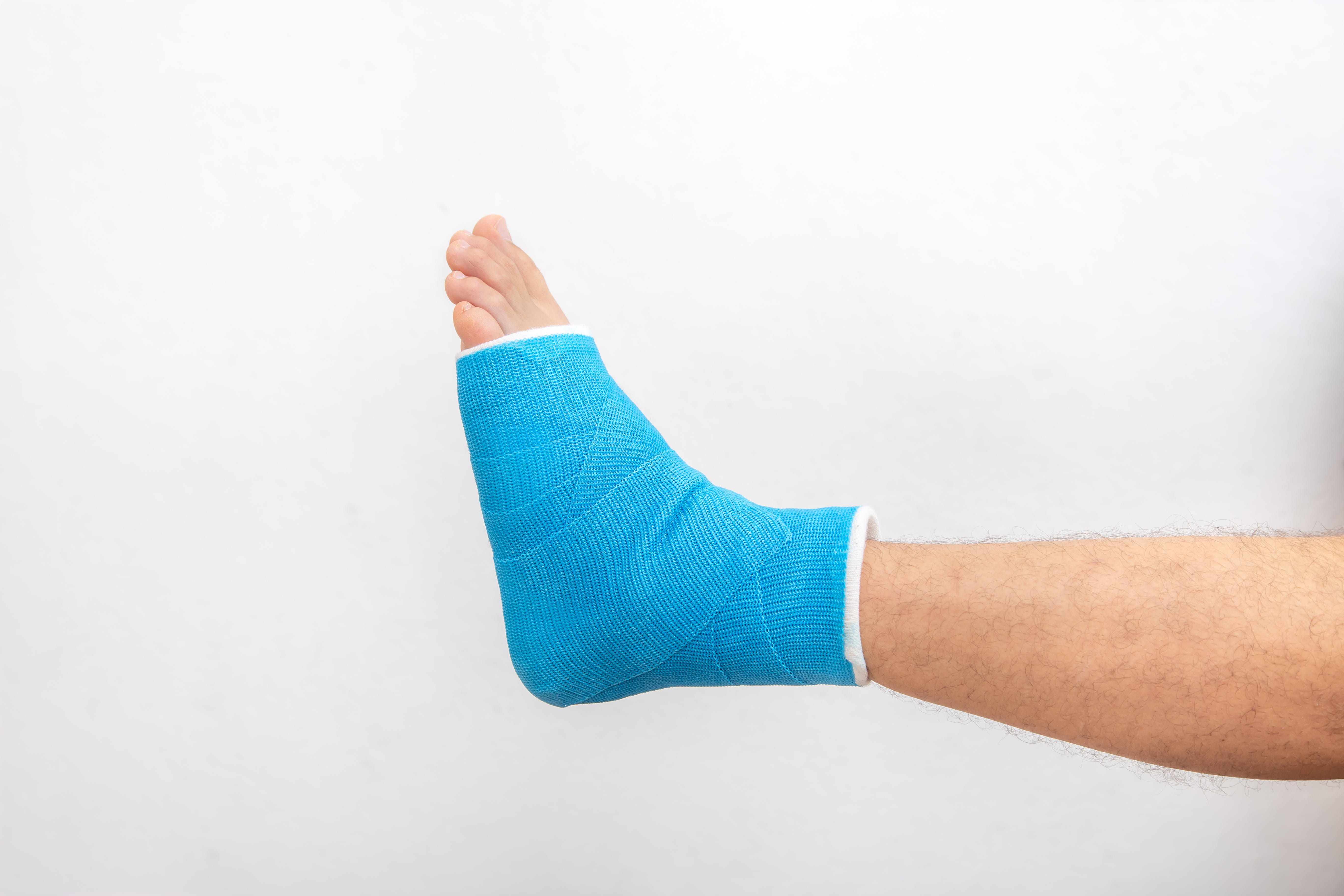
This is the second most common type of break. A bimalleolar ankle fracture occurs when both the inner and outer parts of the ankle bone, known as the malleoli, are broken. The malleoli include the medial malleolus on the inner side (connected to the tibia bone) and the lateral malleolus on the outer side (connected to the fibula bone). When both of these bones are fractured, it can cause severe pain, swelling, and difficulty in walking or bearing weight on the affected leg.
Treatment usually involves surgery to realign and stabilise the broken bones using screws, plates, or wires. This form of break can take two to four months before any weight is able to be out on the ankle and full recovery won’t be completed for four to six months.
Other common ankle break types:
- Medial malleolus fracture: This refers to a fracture of the tibia bone on the inner side of the ankle.
- Trimalleolar fracture: This is a more severe ankle fracture that involves fractures in the lateral and medial malleoli, as well as the outside aspect of the tibia, known as the posterior malleolus.
- Pilon fracture: This is a complex fracture that involves the bottom part of the tibia, usually extending into the ankle joint. It is often caused by high-energy trauma.