Published: October 2025
Last Reviewed: November 2022
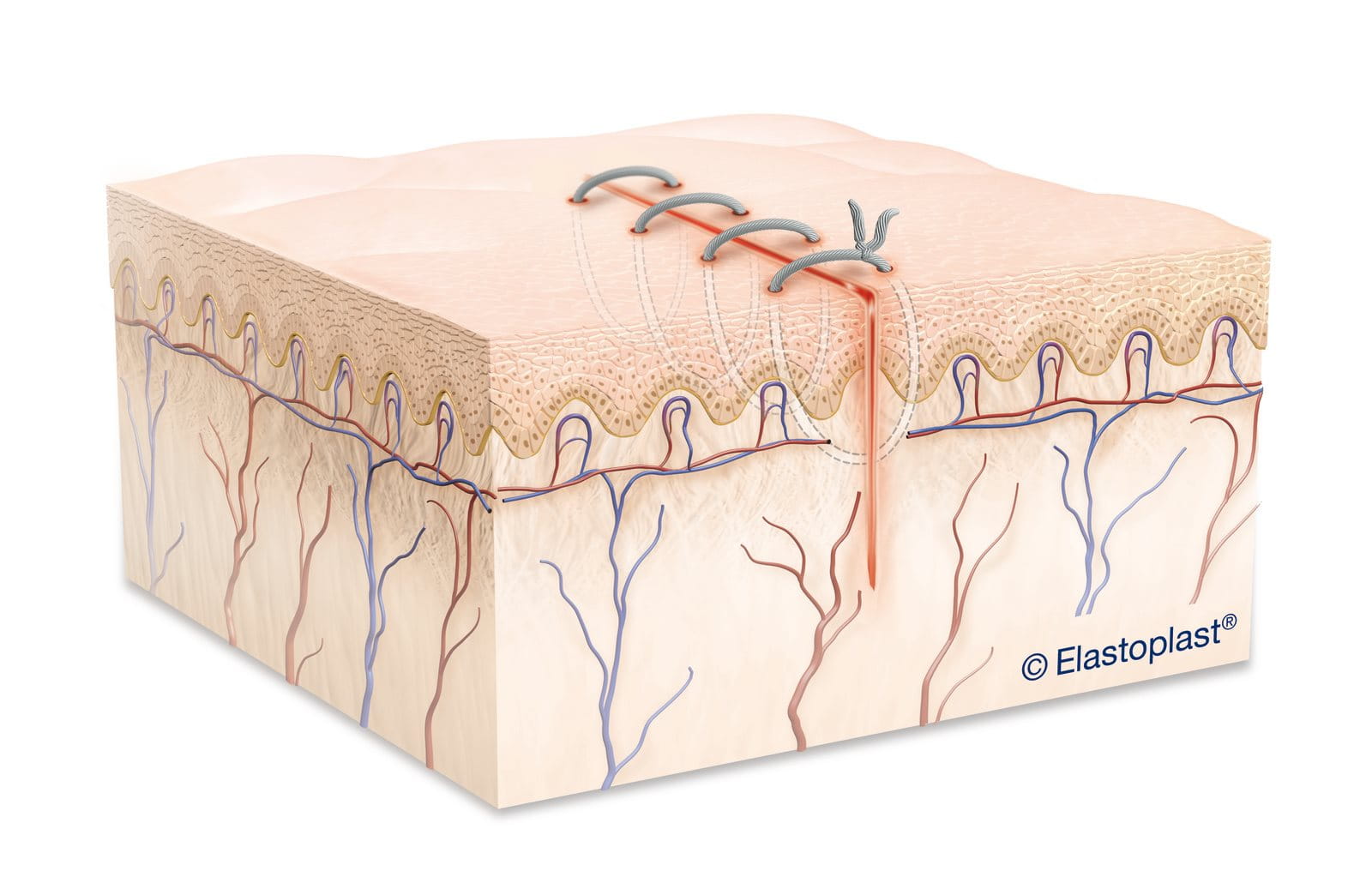
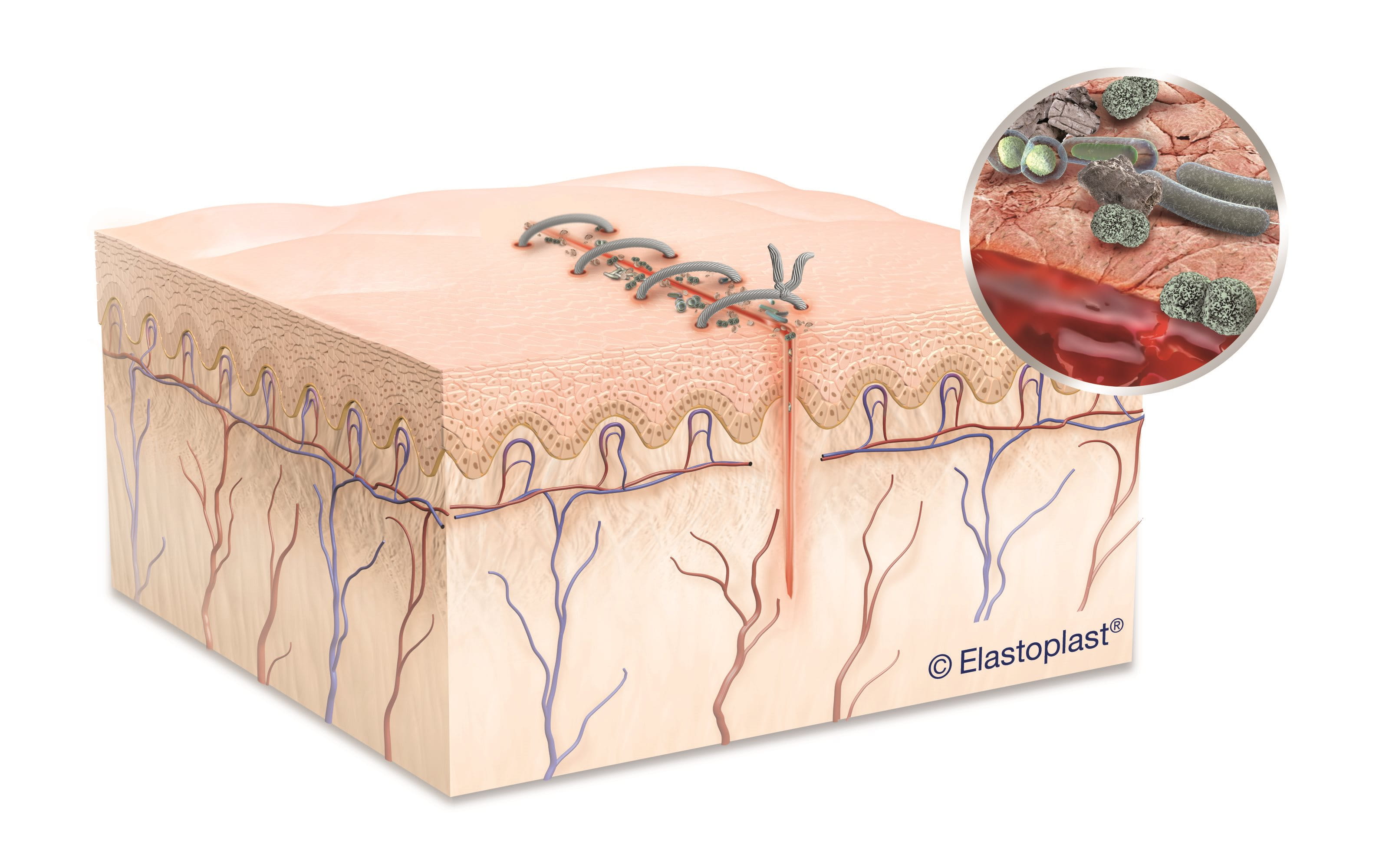
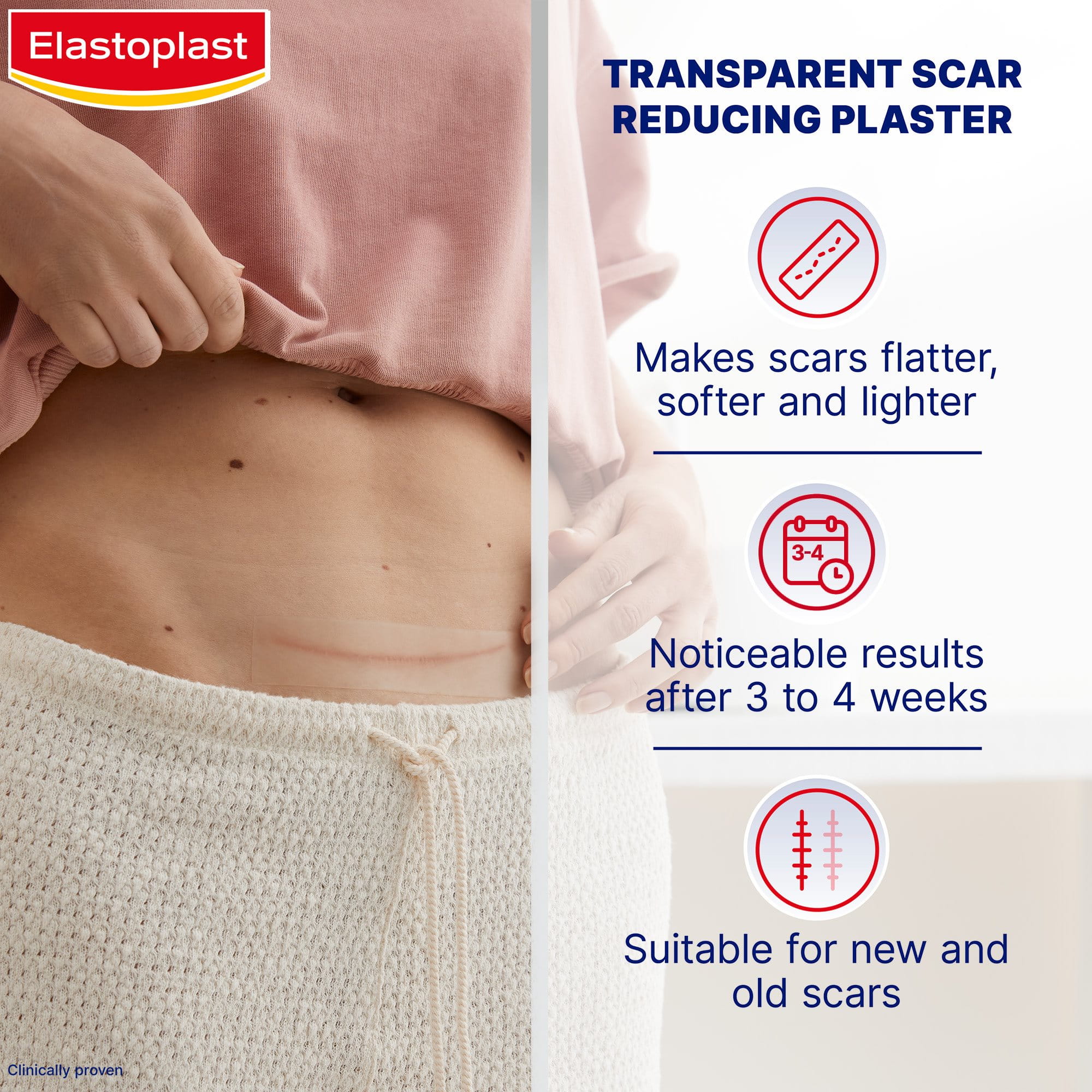
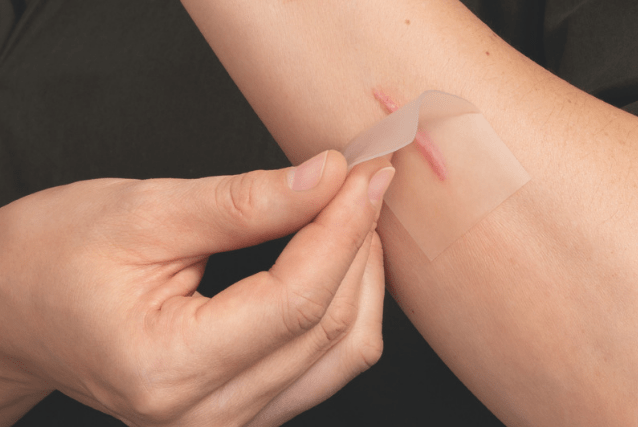
Correct post-surgical wound care is essential to support healing, prevent surgical wound infection, and minimise scarring. Surgical wounds, also known as post-operative wounds, are intentional incisions made during surgery and usually closed with stitches (sutures), staples, or surgical glue.
This guide explains how to clean, protect, and monitor your surgical wound, with practical tips and recommended Elastoplast products.