Published: October 2025
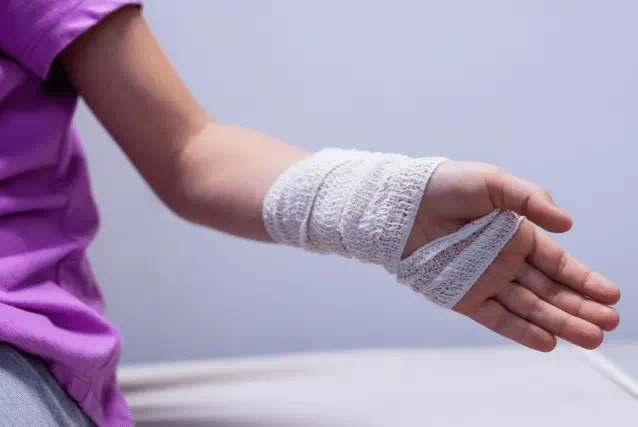
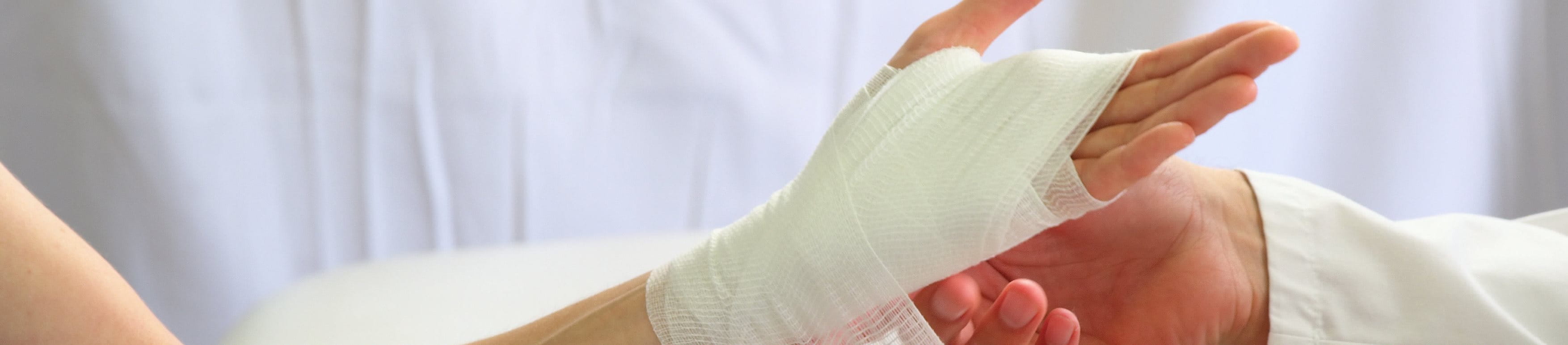
Promptly controlling bleeding is the first step in proper wound care, whether it’s a minor cut or a deeper injury. Taking the right action early not only limits blood loss but also reduces the risk of infection and supports effective healing.
Elastoplast supports safe and effective wound care through three key steps: Clean, Protect, Heal. Following this routine ensures wounds are managed at every stage, helping to prevent complications and promote faster recovery.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to effectively stop bleeding, care for both minor and more persistent cuts, and support long-term wound healing.